Goat Cheese in Different Diets
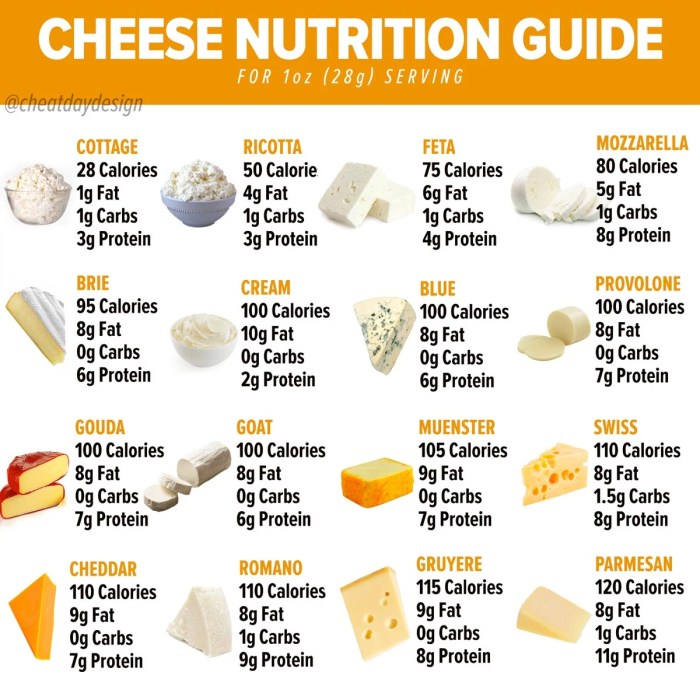
Goat cheese nutrition info – Goat cheese, with its creamy texture and tangy flavor, offers a delightful addition to many meals. However, its suitability varies depending on individual dietary needs and restrictions. Understanding how goat cheese fits into different eating plans is crucial for making informed choices.
Goat cheese’s nutritional profile—rich in protein and calcium, yet relatively lower in fat compared to some cheeses—makes it a versatile ingredient. Its adaptability depends heavily on the type of goat cheese (e.g., soft, firm, aged) and serving size.
Goat Cheese in Ketogenic Diets
The ketogenic diet emphasizes high fat, moderate protein, and very low carbohydrate intake. Goat cheese, particularly the harder varieties, can be a valuable part of a ketogenic diet due to its relatively low carbohydrate content. A small serving adds satisfying creaminess and protein to meals without significantly impacting ketone production. However, it’s important to monitor portion sizes, as even small amounts of carbohydrates can affect ketosis.
For example, a 1-ounce serving of feta (a type of goat cheese) might contain around 1 gram of carbohydrates, which is manageable within a ketogenic macro plan.
Goat Cheese in Mediterranean Diets
The Mediterranean diet is characterized by an abundance of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and healthy fats. Goat cheese fits seamlessly into this dietary pattern. It provides a good source of protein and calcium, complementing the diet’s emphasis on dairy products (preferably from sheep and goats). Goat cheese can be incorporated into salads, dips, or used as a topping for vegetables and grains.
So, you’re lookin’ at goat cheese nutrition info, eh? Makin’ sure your kaki ain’t gettin’ all wobbly from too much cholesterol, right? Well, before you get too caught up in the healthy stuff, consider this: if you’re craving something totally opposite, check out the taco bell chili cheese burrito nutrition – it’s a whole different ball game! But hey, moderation is key, even when comparing goat cheese to a chili cheese burrito explosion; balance is important for a happy tummy, ya tau!
Its use aligns perfectly with the diet’s emphasis on healthy, unprocessed foods.
Goat Cheese in Vegetarian/Vegan Diets
Goat cheese is naturally suitable for lacto-ovo vegetarian diets (those including dairy and eggs). However, it is unsuitable for vegans. For vegans, numerous alternatives exist that offer similar creamy textures and can be used as substitutes in recipes. These include tofu-based cheeses, cashew-based cheeses, or other plant-based cheese alternatives often made from nuts, seeds, or vegetables. These alternatives may not perfectly replicate the taste and texture of goat cheese, but they offer comparable nutritional benefits in terms of protein and calcium, albeit from different sources.
Goat Cheese and Dietary Needs: A Comparison
| Dietary Plan | Suitability | Considerations | Example Serving |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ketogenic | Good (harder varieties) | Monitor carbohydrate intake; choose lower-carb options. | 1 oz feta cheese crumbled on salad |
| Mediterranean | Excellent | Incorporate into salads, dips, or as a topping. | 2 oz soft goat cheese spread on whole-wheat bread |
| Vegetarian | Excellent | Provides protein and calcium. | Goat cheese stuffed peppers |
| Vegan | Unsuitable (plant-based alternatives available) | Consider tofu, cashew, or other plant-based cheeses. | Vegan cashew cheese on crackers |
Goat Cheese vs. Other Cheeses

Goat cheese, with its tangy flavor and creamy texture, holds a special place among cheese lovers. But how does it stack up nutritionally against other popular cheeses? Understanding these differences can help you make informed choices about your diet.Goat cheese boasts a unique nutritional profile compared to its cow’s milk counterparts. While variations exist depending on the type of goat cheese and its production method, general comparisons can be drawn.
Nutritional Differences Between Goat and Cow’s Milk Cheeses
Goat cheese generally has a slightly lower fat content than some cow’s milk cheeses like cheddar, though this can vary considerably depending on the type of goat cheese. However, goat cheese often contains a higher proportion of medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs), which are easier for the body to digest and metabolize. Protein content is fairly comparable across different cheese types, offering a good source of this essential macronutrient.
A key difference lies in the mineral composition. Goat cheese is often richer in certain minerals like calcium and potassium, although the exact amounts vary based on the cheese’s production and aging process. Cow’s milk cheeses, on the other hand, may contain higher levels of other minerals depending on the type.
Comparative Nutritional Profile: A Visual Representation, Goat cheese nutrition info
Imagine a bar graph. The horizontal axis lists four cheese types: Goat Cheese, Cheddar Cheese, Feta Cheese, and Mozzarella Cheese. The vertical axis represents the amount of a nutrient (we’ll use fat content as an example, but this could be repeated for protein or calcium). Each cheese type has a colored bar extending upwards, representing its fat content.
Let’s say Cheddar has the tallest bar, indicating the highest fat content. Goat cheese would have a shorter bar, showing a lower fat content than Cheddar but perhaps slightly higher than Mozzarella. Feta cheese would have a bar of intermediate height. Different colors could represent different cheeses, making the visual comparison clear and easy to understand. This graph could be repeated to illustrate differences in protein and calcium content, with each graph showing a distinct pattern across the four cheeses.
The key is to show the relative differences, not necessarily the exact numerical values.
Commonly Asked Questions: Goat Cheese Nutrition Info
Is goat cheese good for weight loss?
Goat cheese can be part of a weight-loss plan, but portion control is key due to its fat content. Opt for lower-fat varieties and incorporate it mindfully into your overall calorie intake.
Can people with lactose intolerance eat goat cheese?
Some individuals with lactose intolerance tolerate goat cheese better than cow’s milk cheese because it contains different types of lactose and often less of it. However, individual reactions vary, so it’s best to start with a small amount to assess tolerance.
Is goat cheese high in cholesterol?
The cholesterol content of goat cheese varies depending on the fat content. Full-fat varieties will naturally contain more cholesterol than lower-fat options. Individuals concerned about cholesterol should consider their overall dietary intake and consult with a healthcare professional.
How long does goat cheese last?
Properly stored goat cheese can last for several weeks. Keep it refrigerated and tightly wrapped to maintain freshness and prevent spoilage. Check for any signs of mold or off-odors before consumption.



